Childhood Obesity
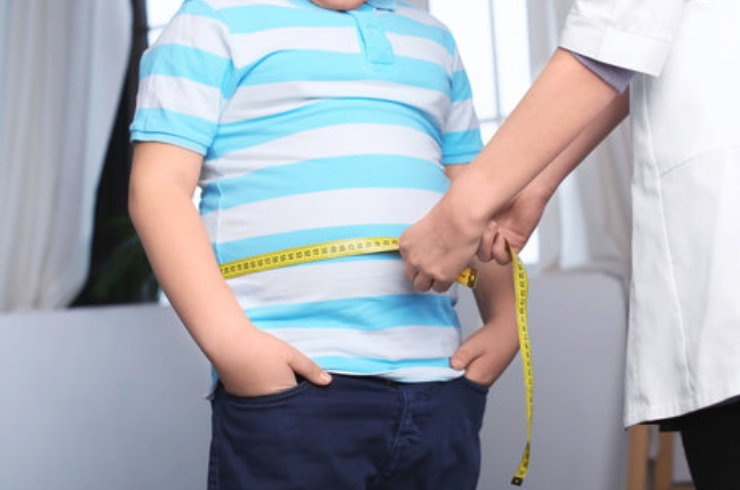

Understanding Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity is a growing health concern that affects many children today. It occurs when a child’s body weight is significantly above the healthy range for their age and height, often due to an imbalance between calories consumed and calories burned. Obesity in childhood can lead to serious health complications such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, asthma, and emotional difficulties like low self-esteem. Recognizing the early signs and addressing the issue promptly is essential to help children achieve a healthier future.
Causes and Risk Factors of Childhood Obesity
Several factors contribute to childhood obesity, including poor eating habits, lack of physical activity, genetic predisposition, and environmental influences. High consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and sedentary lifestyles with excessive screen time are common contributors. In some cases, medical conditions or certain medications can also play a role. Children growing up in families with unhealthy lifestyle habits are at increased risk. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda emphasizes the importance of understanding these factors to develop effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Addressing childhood obesity involves a holistic approach that includes healthy nutrition, regular physical activity, and emotional support. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda recommends creating balanced meal plans rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while limiting sugary and fatty foods. Encouraging at least 60 minutes of active play or exercise daily helps maintain a healthy weight and promotes overall well-being. It is equally important for parents to foster a positive environment that supports healthy habits without focusing solely on weight. Regular medical check-ups and guidance from a pediatrician can help track progress and address any related health issues early. With the right care and lifestyle changes, children can overcome obesity and thrive.
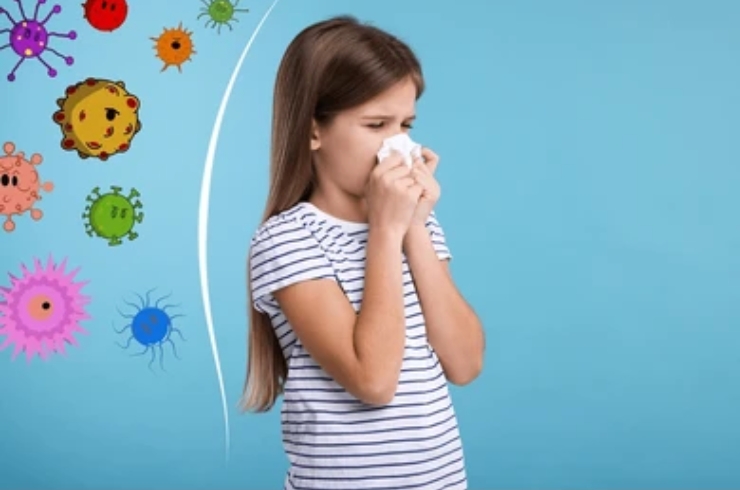

Understanding Respiratory Infections in Children
Respiratory infections are one of the most frequent health challenges affecting children, particularly infants and toddlers whose immune systems are still developing. These infections can involve any part of the respiratory tract, including the nose, throat, airways, and lungs. Common illnesses range from mild colds and sore throats to more serious conditions like bronchitis and pneumonia. Symptoms often include coughing, sneezing, runny nose, fever, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Prompt recognition and appropriate care are crucial to helping children recover quickly and avoid complications.
Causes and Risk Factors of Respiratory Infections
In children, respiratory infections are mainly caused by viruses such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, and influenza, although bacteria can also be responsible in some cases. Young children are especially susceptible due to their immature immune systems and frequent exposure to germs in places like daycare and school. Additional factors that increase vulnerability include exposure to tobacco smoke, existing allergies or asthma, and crowded living environments. Good hygiene practices, avoiding contact with sick individuals, and staying current with vaccinations can help minimize the risk of infection.
Treatment and Prevention: What Parents Should Know
Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda emphasizes that treatment depends on the type and severity of the infection. Mild viral infections often improve with rest, fluids, and fever control, while bacterial infections may require antibiotics. Children with asthma or recurrent infections need close monitoring to prevent flare-ups. Prevention is equally important—parents should encourage frequent handwashing, ensure vaccinations are up to date, avoid smoke exposure, and seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or breathing becomes difficult. With early care and attentive management, respiratory infections in children can be effectively treated to support their overall health and well-being.
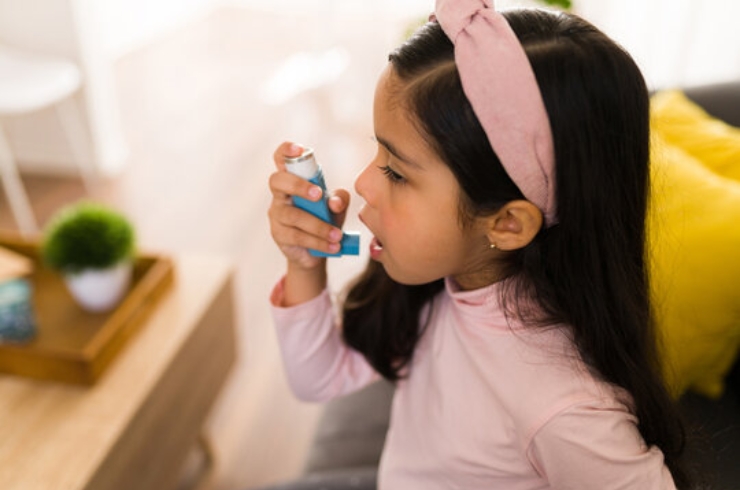

Understanding Asthma in Children
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects many children worldwide. It causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult for children to breathe comfortably. Symptoms of asthma include wheezing, coughing (especially at night or early morning), shortness of breath, and chest tightness. These symptoms can vary in intensity and may be triggered by allergens, respiratory infections, exercise, cold air, or environmental irritants. Early diagnosis and proper management are essential to help children lead active, healthy lives without frequent disruptions caused by asthma attacks.
Causes and Triggers of Pediatric Asthma
Asthma in children is often linked to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A family history of asthma or allergies increases a child’s risk of developing the condition. Common triggers include exposure to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold, tobacco smoke, and air pollution. Respiratory infections, such as colds or flu, can also worsen asthma symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these triggers play a vital role in controlling asthma and preventing flare-ups. Parents should work closely with their pediatrician to understand their child’s specific triggers and develop a personalized asthma action plan.
Effective Asthma Management and Prevention
Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda stresses that asthma management focuses on controlling symptoms, preventing attacks, and maintaining normal lung function. Treatment typically includes daily use of inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and quick-relief inhalers to manage acute symptoms. Regular follow-ups help monitor the child’s condition and adjust treatment as needed. In addition to medication, lifestyle adjustments such as avoiding triggers, maintaining good indoor air quality, and ensuring vaccinations can greatly improve a child’s quality of life. With proper care and vigilance, children with asthma can enjoy an active, fulfilling childhood.
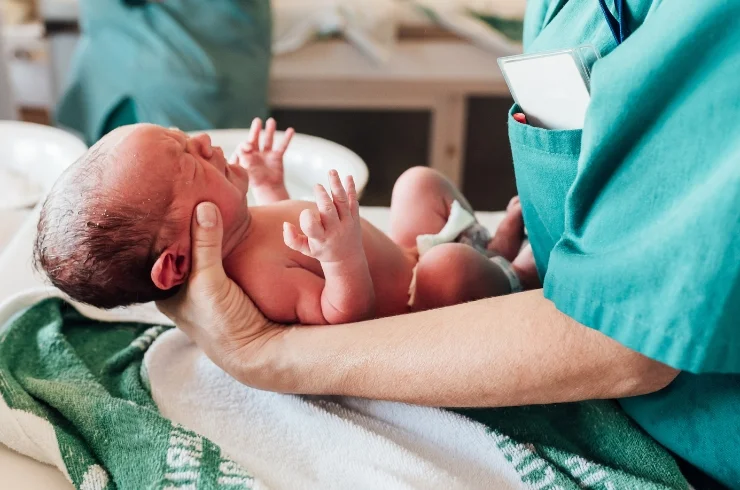

Essential Newborn Care: Nurturing Your Baby’s First Days
The first few weeks of life are critical for a newborn’s growth and development. Proper newborn care lays the foundation for a healthy future, encompassing feeding, hygiene, sleep, and medical monitoring. Understanding these essentials helps parents provide a safe and nurturing environment for their baby during this delicate period.
Feeding and Nutrition for Newborns
Breastfeeding is highly recommended as the ideal source of nutrition for newborns, providing essential antibodies and nutrients that strengthen the immune system. For mothers who cannot breastfeed, suitable alternatives like formula milk ensure the baby receives balanced nutrition. Feeding on demand and recognizing hunger cues promote healthy growth. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda emphasizes the importance of frequent feeding in the early weeks and encourages mothers to seek support for breastfeeding challenges.
Hygiene and Health Monitoring
Newborns require gentle care to maintain hygiene, including regular diaper changes and careful cleaning of the umbilical cord area until it heals. Bathing should be done with mild, baby-safe products. It is important to monitor a newborn for signs of illness such as fever, feeding difficulties, or unusual fussiness. Routine pediatric check-ups allow for early detection of any health concerns and timely immunizations. Dr. Guttikonda advises parents to maintain a clean environment and to limit exposure to infections during these vulnerable early days.
Safe Sleep Practices
Safe sleep is crucial to reduce the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Newborns should sleep on their backs on a firm mattress, without loose bedding or toys in the crib. Establishing a consistent sleep routine supports healthy sleep patterns and overall development. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda guides parents on creating a safe, comfortable sleep environment to ensure restful nights for both baby and family.
Vaccinations for Newborns
Vaccinations protect newborns from serious infections by building immunity early in life. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda recommends timely immunizations following pediatric schedules to ensure your baby’s health and safety.
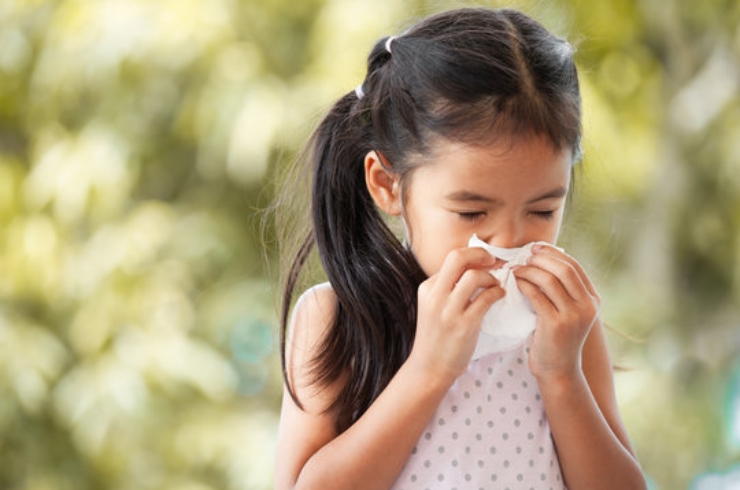

Understanding Allergies in Children
Allergies occur when a child’s immune system overreacts to substances that are typically harmless, known as allergens. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, insect stings, and medications. Allergic reactions can affect various parts of the body, causing symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, skin rashes, hives, digestive issues, and in severe cases, difficulty breathing. Early identification and proper management of allergies are vital to improve a child’s quality of life and prevent complications.
Common Types and Triggers of Pediatric Allergies
Children may experience different types of allergies, including respiratory allergies like hay fever (allergic rhinitis), food allergies, skin allergies such as eczema, and insect bite allergies. Environmental factors such as exposure to pollen, mold, dust mites, and pet hair often trigger respiratory allergies. Food allergies commonly involve peanuts, milk, eggs, and shellfish. Recognizing specific triggers is crucial for effective allergy control. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda advises parents to observe symptoms carefully and seek medical evaluation to identify allergens through testing, enabling targeted treatment plans.
Managing and Preventing Allergies
Managing allergies in children involves a combination of avoiding known allergens, using medications, and sometimes immunotherapy. Treatments may include antihistamines, nasal sprays, or corticosteroids to reduce symptoms and inflammation. In cases of food allergies, strict avoidance of the allergenic food is essential, and parents should be prepared to manage accidental exposure. Dr. Guttikonda emphasizes the importance of educating families about recognizing early signs of severe allergic reactions and knowing when to seek emergency care. Preventive measures such as maintaining a clean environment, reducing exposure to triggers, and keeping vaccinations current can help minimize allergy flare-ups. With proper management, children with allergies can lead healthy, active lives free from frequent discomfort.

Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder in Children
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex developmental condition that affects how a child communicates, interacts socially, and perceives the world. ASD varies widely in its presentation, with symptoms ranging from mild to more pronounced challenges in social communication, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. Early recognition and diagnosis are crucial, as timely intervention can significantly improve a child’s developmental outcomes and quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms of Autism in Young Children
Children with autism may show differences in social interaction, such as limited eye contact, difficulty understanding social cues, or challenges in forming friendships. They might also display repetitive behaviors, intense focus on specific interests, or resistance to changes in routine. Language development may be delayed or unusual, with some children having difficulty expressing needs or emotions. Sensory sensitivities—such as being overwhelmed by loud sounds, bright lights, or certain textures—are also common. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda encourages parents to observe these signs and consult a pediatric specialist for a thorough developmental assessment if concerns arise.
Early Intervention and Support for Autism
Although there is no cure for ASD, early intervention with therapies such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and behavioral interventions can foster skill development and improve social functioning. Dr. Guttikonda emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach tailored to each child’s unique needs. Family education and support are equally important to create an environment where the child can thrive. With early and ongoing care, many children with autism can lead fulfilling lives, achieving their full potential.
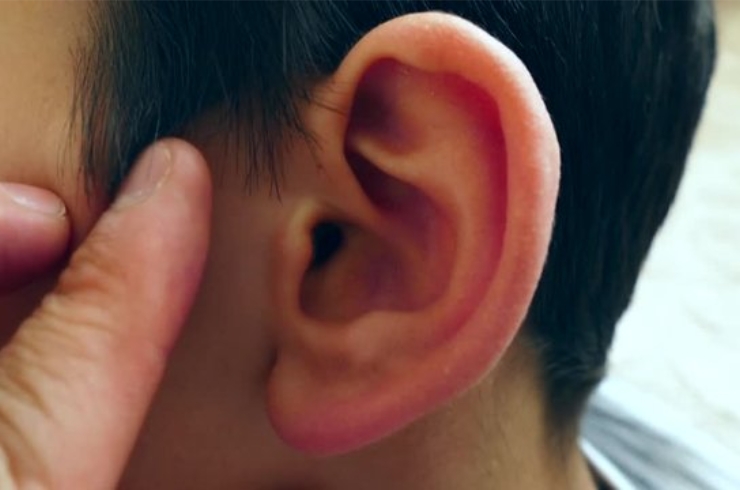
Understanding Ear Infections in Children
Ear infections are one of the most common reasons children visit a pediatrician. These infections occur when bacteria or viruses cause inflammation in the middle ear, leading to pain, swelling, and sometimes fluid buildup behind the eardrum. Young children, especially those under the age of five, are more susceptible due to the structure of their ear canals and developing immune systems. Symptoms often include ear pain, irritability, difficulty sleeping, fever, and sometimes temporary hearing loss. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and support your child’s comfort and recovery.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ear Infections
The middle ear connects to the back of the throat through the Eustachian tubes, which help equalize ear pressure and drain fluid. In children, these tubes are shorter and more horizontal, making it easier for germs to enter and cause infection. Common triggers include respiratory infections such as colds and sinus infections, allergies, and exposure to secondhand smoke. Children who attend daycare or use pacifiers frequently are also at higher risk. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda advises parents to watch for signs of ear infections, especially in infants and toddlers, to ensure timely care.
Treatment and Prevention Tips
Treatment for ear infections depends on the severity and cause. Many mild infections improve without antibiotics, but in some cases, medication may be necessary to clear the infection and relieve pain. Pain management with appropriate fever reducers and warm compresses can help soothe discomfort. Preventive measures include keeping your child’s vaccinations up to date, avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke, and practicing good hand hygiene to reduce the spread of infections. If your child experiences frequent ear infections or hearing difficulties, consulting a pediatric specialist like Dr. Guttikonda is important for further evaluation and management.
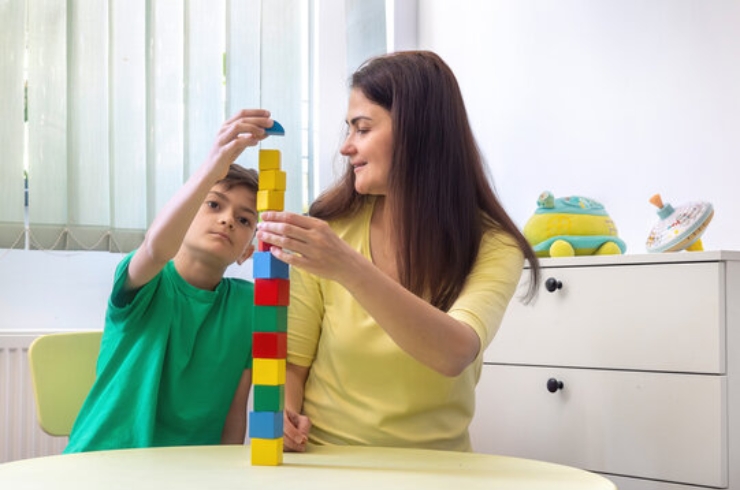

Understanding Developmental Delay in Children
Developmental delay refers to when a child does not reach milestones in motor skills, speech and language, social interaction, or cognitive abilities at the expected age. Every child grows at their own pace, but significant delays in these areas can indicate an underlying issue that needs attention. Early identification is key to providing the necessary support that can help children improve and catch up with their peers. Parents should be aware of typical developmental milestones and consult a pediatrician if they notice persistent delays or concerns.
Common Signs and Causes of Developmental Delay
Children with developmental delays may show difficulties in walking, talking, understanding instructions, or interacting with others. These delays can affect one or more areas of development and vary in severity. Causes include genetic conditions, complications during pregnancy or birth, infections, nutritional deficiencies, or environmental factors such as limited stimulation. Sometimes, delays occur without a known cause. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda stresses the importance of thorough evaluation to determine the cause and plan effective interventions.
Early Intervention and Support Strategies
The earlier developmental delays are detected, the better the chances for improvement. Early intervention programs often involve physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and special education tailored to the child’s specific needs. Dr. Guttikonda works closely with families to create personalized care plans that promote growth and learning. Supportive environments at home and school also play a critical role. Regular monitoring and follow-ups ensure that the child’s progress is tracked and therapies adjusted as needed. With timely care and encouragement, children with developmental delays can achieve meaningful milestones and thrive.
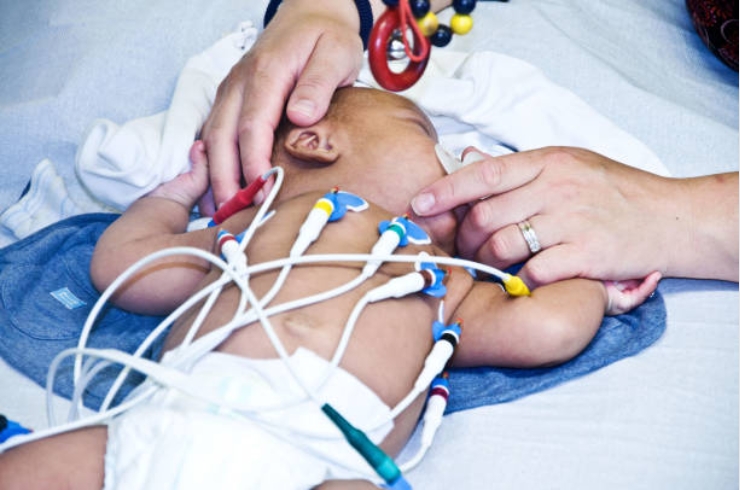
Understanding Congenital Heart Defects in Children
Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) are structural abnormalities of the heart present at birth that can affect how blood flows through the heart and to the rest of the body. These defects range from simple issues that may resolve on their own to complex conditions requiring lifelong medical care or surgery. Early diagnosis is critical to managing CHDs effectively and ensuring the best possible outcomes for affected children.
Types and Symptoms of Congenital Heart Defects
There are many types of CHDs, including holes in the heart (such as atrial septal defects or ventricular septal defects), valve malformations, and abnormalities in the blood vessels connected to the heart. Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of the defect but may include rapid breathing, fatigue, poor feeding, bluish tint to the skin (cyanosis), and failure to thrive. Some defects are detected before birth through prenatal ultrasound, while others become apparent in infancy or early childhood. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda emphasizes the importance of early screening and monitoring to identify CHDs as soon as possible.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing CHDs involves a combination of physical examinations, echocardiograms (ultrasound of the heart), chest X-rays, and sometimes cardiac catheterization or MRI. Treatment depends on the specific defect and may range from medication to manage symptoms to surgical interventions to repair or correct the defect. Many children with CHDs lead active, healthy lives after appropriate treatment and ongoing follow-up care. Dr. Guttikonda advocates for a multidisciplinary approach involving pediatric cardiologists, surgeons, and therapists to ensure comprehensive care tailored to each child’s needs.
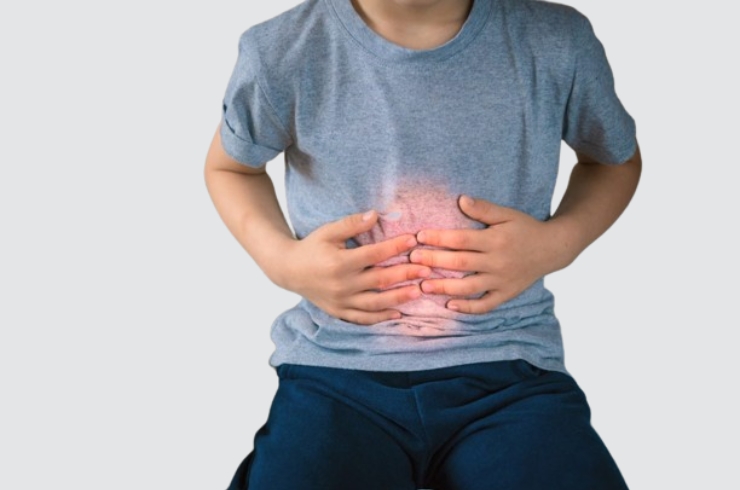
Understanding Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the digestive system, including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas. In children, these disorders can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, and poor appetite. Identifying the underlying cause is essential to provide effective treatment and ensure a child’s proper growth and development.
Common Types and Symptoms of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Disorders
Children may experience various GI conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), constipation, lactose intolerance, celiac disease, and infections like gastroenteritis. Symptoms often include recurrent stomach aches, bloating, changes in bowel habits, and difficulty swallowing. Persistent or severe symptoms warrant evaluation by a pediatrician to diagnose the specific disorder. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda encourages parents to observe any changes in their child’s digestive health and seek medical advice promptly.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and sometimes diagnostic tests like blood work, stool analysis, ultrasound, or endoscopy. Treatment varies depending on the condition and may include dietary modifications, medications, or specialized therapies. For example, children with lactose intolerance benefit from avoiding dairy products, while those with constipation may require increased fiber intake and hydration. Dr. Guttikonda emphasizes the importance of a personalized treatment plan to address each child’s unique needs and promote digestive health. With timely intervention and ongoing care, most children recover well and maintain healthy digestion.
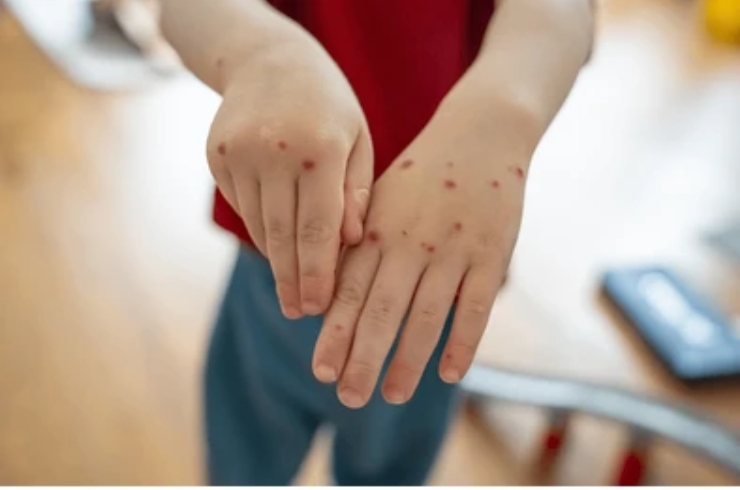
Understanding Pediatric Infectious Diseases
Pediatric infectious diseases encompass a broad spectrum of illnesses caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites that primarily affect children. Due to their developing immune systems, children are particularly vulnerable to these infections, which can range from mild conditions like the common cold to more serious illnesses such as pneumonia, meningitis, or sepsis. Early recognition and appropriate treatment are vital to prevent complications and promote quick recovery.
Common Infectious Diseases in Children
Children often experience infections such as respiratory tract infections, ear infections, gastroenteritis, chickenpox, measles, and urinary tract infections. Vaccination plays a critical role in preventing many of these illnesses. Symptoms vary depending on the infection but may include fever, cough, rash, vomiting, diarrhea, and lethargy. Dr. Harshasree Guttikonda advises parents to monitor symptoms closely and seek timely medical care, especially if a child shows signs of severe illness like difficulty breathing, persistent high fever, or dehydration.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing infectious diseases in children involves a combination of vaccination, good hygiene practices, balanced nutrition, and avoiding exposure to sick individuals. Handwashing, proper sanitation, and safe food handling are essential steps to reduce infection risk. When infections occur, treatment depends on the cause and may include antibiotics, antivirals, or supportive care such as fluids and rest. Dr. Guttikonda emphasizes the importance of following the full course of prescribed medications and attending follow-up visits to ensure complete recovery. With vigilant care and preventive measures, most pediatric infections can be effectively managed, allowing children to grow healthy and strong.